|
This document describes technical details of the system cb_WET
- Web-Tracking and the software cb_WET-server necessary
for it. Introductory information, possible applications, system
prerequisites and the advantages of cb_WET are summarized
in the short info.
Contents
Introduction
cb_WET is a system, which tracks the access to web
pages, writes the resulting data to logfiles and (optionally)
displays the data "live". The logfiles correspond
to the "combined logfile format (DLF)" , standardized
by the W3C. With the use of common logfile-analyzing tools,
the logged data can be processed to any desired report.
cb_WET summarizes the advantages of the methods "webserver
logs" (detailed data in standardized format) and "third
party tracking systems" (relatively simple handling of
the integration in web pages) and offers additional advantages.
All aspects of the data acquisition, as well as the logged
data itself remain under full control of the user of cb_WET.
Mode of operation
The software for the cb_WET-server is installed on
a computer (Windows NT, 2000, XP) inside the target network
(Internet or Intranet). This computer can be an already existing
server.
All web pages, which should be monitored, must be equipped
with a hyperlink to an image file at the cb_WET-server.
This hyperlink can be inserted directly into the HTML code
or it can be generated dynamically (either with a CGI-program
at the server or with Java-Script at the client).
When the webbrowser requests the image file, additional data
is transmitted to cb_WET (in the URL and the HTTP header
of the request).
From the view of the client, the cb_WET-server behaves
like a "normal" webserver, i.e. it returns the requested
image file. The fundamental difference however is, that the
server always returns the same image file, independently of
the requested URL. The data, which was transmitted by the
client (with the the request), is analyzed, completed if necessary,
written to the logfile and displayed on the userinterface.
Restrictions
All methods, which use hyperlinks to image files to count
access to web pages (like cb_WET), will not work for
clients, which do not load image files. This case can arise,
if the client is a textbased browser (quite uncommon today),
or if the loading of images was deactivated by the user. Even
cb_WET can not solve this problem.
Beyond that all other methods (e.g. webserver logs) will
deliver inaccurate results, if a HTTP request from a client
is "intercepted" by a HTTP cache (e.g. from a proxy
server or from browser internal caches). This problem is solved
by cb_WET with certain methods (e.g. parameters in
the HTTP response), details see below.
Recorded data
During a HTTP request the following data is (usually) available
for the server:
- IP address of the client (can be used to determine the
hostname) or an intermediate proxy
- URL (path and filename) of the requested document, possibly
additional parameters in the URL
- HTTP header parameters (e.g. user agent, referrer etc.)
- timestamp of the request
When using cb_WET, any further information can be
"packed" into the URL and/or the URL parameters.
This additional information will also be logged and is available
for later analyses. This concept is called "virtual URLs"
(see below).
Image file
Although any image file (e.g. a logo) could be used with
cb_WET, tracking systems usually use "invisible
images" (imagesize 1 x 1 pixels, transparent color).
Virtual URLs
The cb_WET-server works independently of the requested
URL, i.e. it ignores the path, the filename and the URL parameters
in the request and always returns the same image file (however
the requested URL will be logged "normally").
This means, that the client can request "virtual URLs"
(nonexisting files in nonexisting directories) and nevertheless
receives a valid (and meaningful) response (a normal webserver
would react with an error message).
Because of the fact, that the user of cb_WET can specify
the hyperlink in any way, the path information, the filename
and the URL parameters can be used to "encode" any
arbitrary additional information.
The concept of the virtual URLs can be used for flexible
types of data collection. An obvious application is the creation
of own logical structures for logging and analyses, which
is completely independent of the directory/file structures
of the webservers. See the following examples:
- Logically connected web pages (e.g. for a product, a project,
a department ...), which are located in different directories,
can be mapped to common (virtual) directories.
- Webpages, which are identical (e.g. on mirror servers)
can be mapped to the same (virtual) file.
- Tracking information from several websites, located on
different servers, can be collected in a central point.
- When using HTML mailings, the data can be mapped to own
directories (e.g. either per mailing or per recipient).
Served Files
To allow cb_WET to "behave" like a normal
webserver (e.g. when queried from search engines), it is possible
to add the files "robots.txt" and "index.htm".
The following table shows, which files are served under which
conditions:
| requested document |
returned file |
remarks |
| any file with extension ".gif" on any path |
1x1.gif |
if present, else http error 404 (not found) |
| "robots.txt" |
robots.txt |
if present, else http error 404 (not found) |
| none ("/") or "index.htm" |
index.htm |
if present, else http error 404 (not found) |
| any other file |
- |
http error 404 (not found) |
cb_WET reacts only to http GET and HEAD requests.
POST, PUT, OPTIONS and TRACE requests will not be answered.
Integration of cb_WET-Code into
HTML files
In order to define a hyperlink from a web page (which shall
be monitored) to cb_WET, HTML code has to be inserted
into the page. For static pages this is done directly in the
web page, for dynamically generated pages this is done in
the template or the corresponding script.
Independently of static or dynamic pages there are two types
of cb_WET hyperlinks: the "static" and the
"dynamic" link.
Static link
To use a static link, the following code has to be inserted
into the HTML page (e.g. shortly before the </BODY>
tag). Example:
<img src="http://test.baumann.at/tracking/logo.php/wbat_logo.gif"
alt="cblogo" width="1" height="1">
When a browser sends a request, the following data is available
to the cb_WET-server. Example:
Timestamp: 2002/03/10 19:27:32:885
From: eftp2b.ift.tuwien.ac.at [128.130.106.81]
Command: GET
Document: /wbat_logo.gif
Host: test.baumann.at:88
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.0;
en-US; rv:0.9.8) Gecko/20020204
Accept: text/xml,application/xml,application/xhtml+xml,text/html;q=0.9,text/plain;q=0.8,video/x-mng,image/png,image/jpeg,image/gif;q=0.2,text/css,*/*;q=0.1
Accept-Language: en-us
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress;q=0.9
Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1, utf-8;q=0.66, *;q=0.66
Keep-Alive: 300
Connection: keep-alive
Referer: http://www.baumann.at/downloads/index.html
This data shows (among other information), which computer
("From") requested which web page ("Referer"),
when ("Timestamp"), which browser ("User-Agent"),
...
Dynamic link
This method uses Javascript to build the hyperlink on the
client side (inside the browser). As Javascript has access
to further information of the webbrowser, the link can be
extended and additional information can be added to the request.
To cover the case, that Javascript is "missing"
at the client (either not available or deactivated), also
a static link is inserted.
Example:
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript">
<!--
var Dat="";
Dat += "doctitle=" + escape(document.title);
Dat += "&docurl=" + window.document.URL;
Dat += "&referrer=" + window.document.referrer;
document.write('<img src="http://test.baumann.at/tracking/logo.php/cbnet_DAT.gif?'
+ Dat + '" alt="logo" width="1" height="1">');
//-->
</SCRIPT>
<NOSCRIPT>
<img src="http://test.baumann.at/tracking/logo.php/cbnet_cb_pmm_description.gif"
alt="cbnet_logo" width="1" height="1">
</NOSCRIPT>
</body>
When the browser sends the request, the following information
is available for the server:
2002/03/10 19:31:17:337
From: eftp2b.ift.tuwien.ac.at [128.130.106.81]
Command: GET
Document: /cbnet_DAT.gif
doctitle=creativebytes.net - cb_PMM - Description
docurl=http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/
referrer=http://www.google.com/search?hl=en
q=+"port mapping" +"connection monitoring"
Host: test.baumann.at:88
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.0;
en-US; rv:0.9.8) Gecko/20020204
Accept: text/xml,application/xml,application/xhtml+xml,text/html;q=0.9,text/plain;q=0.8,video/x-mng,image/png,image/jpeg,image/gif;q=0.2,text/css,*/*;q=0.1
Accept-Language: en-us
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress;q=0.9
Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1, utf-8;q=0.66, *;q=0.66
Keep-Alive: 300
Connection: keep-alive
Referer: http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/
The italically marked data corresponds to the
additional information, which was generated by Javascript,
the other data contains the same information as the request
from a static link (see example above).
The additional data in this example: Title of the document,
original URL of the document, "last" referrer (i.e.
which page was linked to this page - in this example the page
was called from the result page of a search engine).
The link to the cb_WET-server can be extended with
any information, which is available for Javascript (e.g. further
details about type and version of the browser, screen resolution,
local time at the client ...).
Remarks: Personal information, like entries of the history
list, email address of the user etc., are NOT available in
current implementations of Javascript.
cb_WET-server
Installation
To install the cb_WET-server just copy all files from
the installation file (.zip) to a directory of your choice
(e.g.: "C:\Program Files\cb_WET). If necessary create
a shortcut on the desktop.
Remark: The imagefile must be in the same directory as the
program and must have the name "1x1.gif". If the
files "index.htm" and "robots.txt" shall
be used, they also have to reside in this directory.
Starting the server:
- Start the program by executing "cb_WET.exe"
- Set the listening port number (default: 88)
- Activate the integrated HTTP-server by pressing the "Start"
button.
The Userinterface
The programs user interface is divided into two pages: "Settings"
(Configuration) and "Logging".
The "Settings"-page
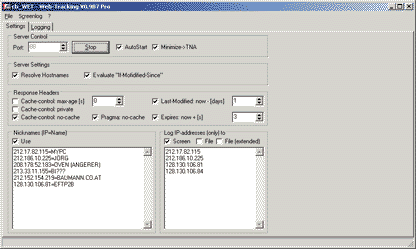
The "Settings"-page provides the following functions
and settings:
Port: The listening port of the integrated HTTP-server.
A certain port can be assigned to one application only. If
a webserver runs on the target machine, it usually uses port
80. cb_WET MUST be configured to use another port,
the default port is 88. The value in the input field can only
be changed, when the server is not active.
Start/Stop: This functions controls the integrated
HTTP-server. Messages about its state and any errors are being
logged to the text field "Messages".
AutoStart: If this option is set, the server will
be activated automatically during the next start of the program.
Minimize->TNA: If this option is selected, the
minimize function will send the program to the "Taskbar
Notification area" (the "Icon Tray"). In combination
with AutoStart cb_WET will minimize to the TNA automatically
on startup.
Set Log Dir: This options allows to change the directory
of the logfiles. If no directory is selected, or the selected
directory is invalid, the logfiles are written to the program's
directory.
Resolve Hostnames: This parameter controls, whether
cb_WET tries to resolve hostnames from the clients
IP-addresses (this function requires DNS and can mean a certain
delay per request).
Evaluate If-Modified-Since: This option controls,
whether cb_WET acts conforming to HTTP (i.e. honours
a "If-Modified-Since" header and returns "304
not modified", if appropriate), or not (ignores the header
and always returns the image file).
The settings for the Response-Header Parameters
- Cache-Control: max-age, private, no-cache
- Pragma: no-cache
- Last-Modified and
- Expires
control the operation and the HTTP response of cb_WET-server.
With optimized parameters it can be achieved, that almost
every client request is forwarded (and captured) by cb_WET-server
and not intercepted by (caching) proxies or browser internal
cache mechanisms.
The default settings are: "Cache-Control: no-cache",
"Pragma: no-cache", "Last-Modified: [now -
1 day]" and "Expires: [now + 3 sec].
Nicknames: To mark clients with certain IP-addresses
(e.g. own computers) within the screenlog, nicknames can be
assigned to those addresses. The entries must use the format
"IP-Adresse=Nickname" (Example: 192.168.1.3=MyPC).
The option "Use" controls the Nickname function.
Log IP-addresses (only) to: This setting can be used
to define certain clients (identified by their IP-addresses)
which requests shall not be logged generally (e.g. own development
systems, certain clients during tests etc.). The defined rules
can be overridden for each "logging-target" ("Screen",
"File" and "File (extended)")
individually.
All configuration settings (except "Port") can
be changed while the server is running. To write the changes
to the configuration file the function "Save Config"
is used.
The"Logging"-page
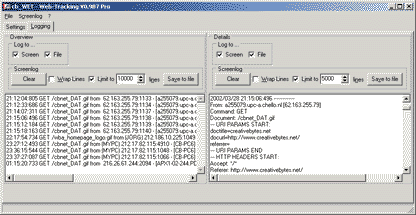
The Logging-page is divided into two sections, corresponding
to the types of logging information in cb_WET: "Overview"
und "Details" (extended logging). The content
of the displayed information is identical with the corresponding
logfiles (see later), only the format varies slightly.
The configuration settings and the functions are the same
for both parts of the screenlog:
The options "Log to ..." define (for each
logtype), whether the data is written to the screenlog and/or
the logfile.
To limit the memory usage of the program, the number of lines
in the screenlogs can be limited. This means, that the first
lines are deleted automatically, when the limit is reached.
The number of lines is no exact value, it can vary ca. +/-
5%. Warning: If the limit is deactivated, the screenlog will
grow, until all of the the systems memory is consumed!
The screenlogs text fields are editable and can be used for
clipboard functions (copy/paste). The screenlogs can be cleared
any time (function "Clear") and written to
files ("Save to file") which are independent
of the screenlog files.
Logfiles
The filenames of the logfiles are generated automatically
from the system date ("YYYYMMDD"), the files are
stored in the configured directory. The used file extensions
are: ".LOG" for the file in DLF-format and ".LOG2"
for the extended format.
Logging-Overview
An entry in this format contains the following data:
- Comuter name or IP-address of the client (or the proxy)
- Time stamp
- Requested URL (incl. parameters in encoded format)
- Protocol version
- HTTP status code
- Size of the transferred file
- Referrer (page to measure)
- UserAgent (name and details of the used webbrowser)
The logfile (".LOG") is saved using the DLF-format,
it can be processed with all common analysing tools.
Example for a line in the logfile (shown with linebreaks):
12345.xxx.yyy.net - - [28/Mar/2002:15:31:40 +0100]
"GET /cbnet_DAT.gif doctitle=creativebytes.net%20-%20cb_PMM%20-%20Description&docurl=http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/index.htm&
referrer=http://www.winsite.com/bin/Info?6500000036224 HTTP/1.1"
200 807 "http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/index.htm"
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.0; Windows 98; DigExt)"
Remark: The URL parameters in this example have been transmitted
by a dynamically generated link (using Java script, see above).
Logging-Detail
This logging type contains the following information in addition
to the simple log format:
- IP-address of the client (additionally, if hostname is
available)
- HTTP command (GET or HEAD)
- URL parameters in decoded format
- HTTP headers inside the client request
The extended logfile (".LOG2") is written in the
following format (example):
2002/03/28 15:31:40:105 --------------
From: 12345.xxx.yyy.net [123.123.123.123]
Command: GET
Document: /cbnet_DAT.gif
--- URI PARAMS START:
doctitle=creativebytes.net - cb_PMM - Description
docurl=http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/index.htm
referrer=http://www.winsite.com/bin/Info?6500000036224
--- URI PARAMS END
--- HTTP HEADERS START:
Accept: */*
Referer: http://www.creativebytes.net/cb_PMM/index.htm
Accept-Language: en-us
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.0; Windows 98;
DigExt)
Host: test.baumann.at:88
Connection: Keep-Alive
--- HTTP HEADERS END
The screenlog "Details" also displays the (generated)
HTTP response header after the request data. This information
can be used to check the effect of different settings for
the HTTP response parameters.
Example:
--- RESPONSE HEADER START:
200 OK
Date: Thu, 28 Mar 2002 14:31:40 GMT
Connection: close
Cache-Control: no-cache
Pragma: no-cache
Expires: Thu, 28 Mar 2002 14:31:43 GMT
Last-Modified: Tue, 26 Mar 2002 23:00:00 GMT
--- RESPONSE HEADER END
System-Log
The Messages, displayed on the "Setting"-page of
the program (information about start/stop of cb_WET
server and any error messages) are written into another logfile
(extension ".SYSLOG").
Example:
2002/03/22 16:22:43:375: cb_WET V0.9B6 Pro - Program
started
2002/03/22 16:22:43:515: Trying to start server ...
2002/03/22 16:22:43:546: Server started, listening on 0.0.0.0:88.
2002/03/22 16:23:09:484: Trying to stop server ...
2002/03/22 16:23:09:734: Server stopped.
2002/03/22 16:23:09:734: cb_WET V0.9B6 Pro - Program stopped
2002/03/22 17:02:04:796: cb_WET V0.9B6 Pro - Program started
2002/03/22 17:02:04:937: Trying to start server ...
2002/03/22 17:02:04:984: Server started, listening on 0.0.0.0:88.
2002/03/22 17:02:37:906: Trying to stop server ...
2002/03/22 17:02:38:156: Server stopped.
2002/03/22 17:02:38:156: cb_WET V0.9B6 Pro - Program stopped
Licensing
cb_WET is available in two different versions: The
Light-Version is FREEWARE, The Pro-Version (with
extended features) is SHAREWARE.
Feature Matrix:
| |
Light-Version (FREEWARE)
|
Pro-Version (SHAREWARE)
|
|
limited operation (per program start)
|
max. 100 requests or one hour
|
no limits
|
| log to files (DLF and details) |
yes
|
yes
|
| log to screen |
yes
|
yes
|
| save screenlogs to file |
no
|
yes
|
| configurable limit for screenlogs |
no (100/1000 lines)
|
yes
|
| "unlimited" screenlogs |
no
|
yes
|
| clipboard functions in screenlogs |
no
|
yes
|
| "Autostart" feature |
no
|
yes
|
| multi instance allowed |
no
|
yes
|
| minimize to taskbar notification area |
no
|
yes
|
The Pro-Version can be licensed with our secure
order form at ShareIt!.
Plans for next release:
The next version of cb_WET will use a XML format for
the extended logging information, this format will improve
further processing (e.g. with own programs).
The logging function (currently only DLF) will be configurable
to switch between DLF, CLF and ELF compatible logfiles.
Comments, suggestions and ideas? office@creativebytes.net
|